Mybatis对数据库的单表CUDA操作
1. 配置Mybatis的主配置文件SqlMapConfig,配置数据库的基本信息以及操作的映射配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!-- mybatis的主配置文件 -->
<configuration>
<!-- 配置环境 -->
<environments default="mysql">
<!-- 配置mysql的环境-->
<environment id="mysql">
<!-- 配置事务的类型-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!-- 配置数据源(连接池) -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 配置连接数据库的4个基本信息 -->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_mybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 指定映射配置文件的位置,映射配置文件指的是每个dao独立的配置文件 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="bjtu/dao/UserDao.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
2. 实现User类,定义类属性,和数据库表user中的列值对应
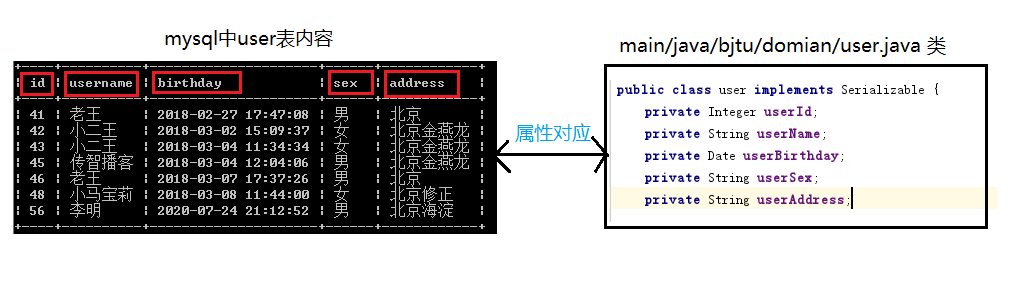
3. 实现操作接口UserDao,定义每个操作数据库的方法
public interface UserDao {
/*
查询所有操作
*/
//@Select("select * from user")
List<user> findAll();
/**
* 保存user
* @param u
*/
void saveUser(user u);
/**
* 更新信息
* @param u
*/
void updateUser(user u);
/**
* 删除用户
* @param userID
*/
void deleteUser(Integer userID);
/**
* 按ID查询用户信息
* @param userID
*/
user findById(Integer userID);
/**
* 按名称模糊查询用户信息
*/
List<user> findByName(String username);
/**
* 聚合函数:查询总记录条数
*/
int findTotal();
}
4. 将UserDao中的每个方法在映射配置文件UserDao.xml中进行配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="bjtu.dao.UserDao">
<!--配置查询结果的列名与实体类的属性名的对应关系-->
<resultMap id="userMap" type="bjtu.domain.user">
<!-- 主键字段的对应-->
<id property="userId" column="id"></id>
<!-- 非主键字段的对应-->
<result property="userName" column="username"></result>
<result property="userBirthday" column="birthday"></result>
<result property="userSex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="userAddress" column="address"></result>
</resultMap>
<!--配置查询所有-->
<select id="findAll" resultMap="userMap">
select * from user
</select>
<!--插入保存用户-->
<insert id="saveUser" parameterType="bjtu.domain.user">
<!--配置插入数据后,获取新增数据的id-->
<selectKey keyProperty="id" keyColumn="id" resultType="int" order="AFTER">
select last_insert_id()
</selectKey>
insert into user(username,address,sex,birthday) values(#{username},#{address},#{sex},#{birthday})
</insert>
<!--更新用户信息-->
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="bjtu.domain.user">
update user set username=#{username},address=#{address},sex=#{sex},birthday=#{birthday} where id=#{id}
</update>
<!--删除用户-->
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="int">
delete from user where id=#{uid}
</delete>
<!--按ID查询一个用户的信息-->
<select id="findById" parameterType="int" resultMap="userMap">
select * from user where id=#{uid}
</select>
<!--按名称模糊查询用户信息-->
<select id="findByName" parameterType="string" resultMap="userMap">
select * from user where username like #{name}
</select>
<!--利用聚合函数查询总记录条数-->
<select id="findTotal" resultType="int">
select count(id) from user
</select>
</mapper>
其中 resultMap 是用来将User类中的属性名和mysql中user表中的类名对应:
<resultMap id="userMap" type="bjtu.domain.user">
<!-- 主键字段的对应-->
<id property="userId" column="id"></id>
<!-- 非主键字段的对应-->
<result property="userName" column="username"></result>
<result property="userBirthday" column="birthday"></result>
<result property="userSex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="userAddress" column="address"></result>
</resultMap>
5. 在test目录下写测试程序 MybatisTest.java
public class MybatisTest {
private InputStream in;
private SqlSession sqlSession;
private UserDao userDao;
@Before
public void init() throws Exception{
//1. 读取配置文件
in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//2. 获取SqlFactorySession
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
//3. 获取SqlSession对象
sqlSession = factory.openSession();
//4. 获取dao的代理对象
userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
}
@After
public void destory() throws Exception{
sqlSession.commit();
//释放资源
sqlSession.close();
in.close();
}
/*
测试查询所有数据功能
*/
@Test
public void testFindAll() throws Exception{
List<user> users = userDao.findAll();
for(user u: users){
System.out.println(u);
}
}
/*
测试保存功能
*/
@Test
public void testSave() throws Exception{
user u = new user();
u.setUserName("李明");
u.setUserAddress("北京海淀");
u.setUserSex("男");
u.setUserBirthday(new Date());
System.out.println("Before saving:"+u);
userDao.saveUser(u);
System.out.println("After saving:"+u);
}
/**
* 测试更新信息功能
*/
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
user u = new user();
u.setUserId(49);
u.setUserName("Mybatis");
u.setUserAddress("bjtu");
u.setUserSex("m");
u.setUserBirthday(new Date());
userDao.updateUser(u);
}
/**
* 测试删除功能
*/
@Test
public void testDelete(){
userDao.deleteUser(57);
}
/**
* 按ID查询一个用户的信息
*/
@Test
public void testFindOne(){
user u = userDao.findById(48);
System.out.println(u);
}
/**
* 按名称模糊查询用户的信息
*/
@Test
public void testFindByName(){
List<user> users = userDao.findByName("%王%");
for(user u: users){
System.out.println(u);
}
}
/**
* 利用聚合函数查询总记录的条数
*/
@Test
public void testFindTotal(){
int s = userDao.findTotal();
System.out.println("总记录条数:"+s);
}
}
Mybatis连接池和事务
事务
在Mybatis的SqlMapConfig.xml配置文件中,通过
来实现Mybatis中连接池的配置。 type属性的三种取值:
- UNPOOLED 不使用连接池的数据源
- POOLED 使用连接池的数据源
JNDI 使用JNDI实现的数据源
MyBatis内部分别定义了实现了java.sql.DataSource接口的UnpooledDataSource,PooledDataSource类来表示UNPOOLED、POOLED类型的数据源。
事务
什么是事务?
事务的四大特性:ACID
不考虑隔离就产生的三个问题
解决方法:四种隔离级别
Mybatis多表查询
1. 数据库创建表
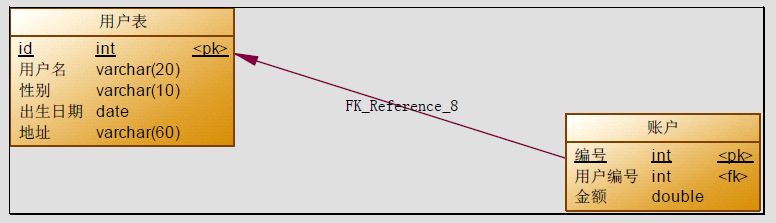
在数据库中创建user、account和role两个表,并设置外键关联。
1)创建user表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL auto_increment,
`username` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户名称',
`birthday` datetime default NULL COMMENT '生日',
`sex` char(1) default NULL COMMENT '性别',
`address` varchar(256) default NULL COMMENT '地址',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
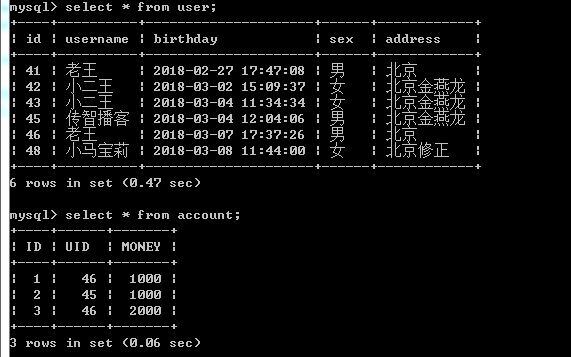
insert into `user`(`id`,`username`,`birthday`,`sex`,`address`) values (41,'老王','2018-02-27 17:47:08','男','北京'),(42,'小二王','2018-03-02 15:09:37','女','北京金燕龙'),(43,'小二王','2018-03-04 11:34:34','女','北京金燕龙'),(45,'传智播客','2018-03-04 12:04:06','男','北京金燕龙'),(46,'老王','2018-03-07 17:37:26','男','北京'),(48,'小马宝莉','2018-03-08 11:44:00','女','北京修正');
2) 创建account表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `account`;
CREATE TABLE `account` (
`ID` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '编号',
`UID` int(11) default NULL COMMENT '用户编号',
`MONEY` double default NULL COMMENT '金额',
PRIMARY KEY (`ID`),
KEY `FK_Reference_8` (`UID`),
CONSTRAINT `FK_Reference_8` FOREIGN KEY (`UID`) REFERENCES `user` (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into `account`(`ID`,`UID`,`MONEY`) values (1,46,1000),(2,45,1000),(3,46,2000);
3)创建role表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `role`;
CREATE TABLE `role` (
`ID` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '编号',
`ROLE_NAME` varchar(30) default NULL COMMENT '角色名称',
`ROLE_DESC` varchar(60) default NULL COMMENT '角色描述',
PRIMARY KEY (`ID`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into `role`(`ID`,`ROLE_NAME`,`ROLE_DESC`) values (1,'院长','管理整个学院'),(2,'总裁','管理整个公司'),(3,'校长','管理整个学校');
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user_role`;
CREATE TABLE `user_role` (
`UID` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户编号',
`RID` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '角色编号',
PRIMARY KEY (`UID`,`RID`),
KEY `FK_Reference_10` (`RID`),
CONSTRAINT `FK_Reference_10` FOREIGN KEY (`RID`) REFERENCES `role` (`ID`),
CONSTRAINT `FK_Reference_9` FOREIGN KEY (`UID`) REFERENCES `user` (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into `user_role`(`UID`,`RID`) values (41,1),(45,1),(41,2);DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `role`;
2. 一对一和一对多查询
本次案例主要以最为简单的用户和账户的模型来分析Mybatis 多表关系。 用户为User 表,账户为Account表。一个用户(User)可以有多个账户(Account)。
准备:
1. 建立两张表:用户表(User)和账户表(Account)
让用户和账户表之间具有一对多的关系,需要外键在账户表中添加
2. 简历两个实体类:用户实体类和账户实体类
让用户和账户实体类中体现一对多的关系
3. 建立两个配置文件:
用户配置文件
账户配置文件
4. 实现配置
当查询用户时,可以同时得到用户下所包含的账户信息
当查询账户时,可以同时得到账户所属的用户信息
账户一对一对应用户,AccountDao.xml查询配置文件

用户一对多用户
1)首先要在User类中增加user与account一对多关系,即一个用户下有多个accounts,用集合封装。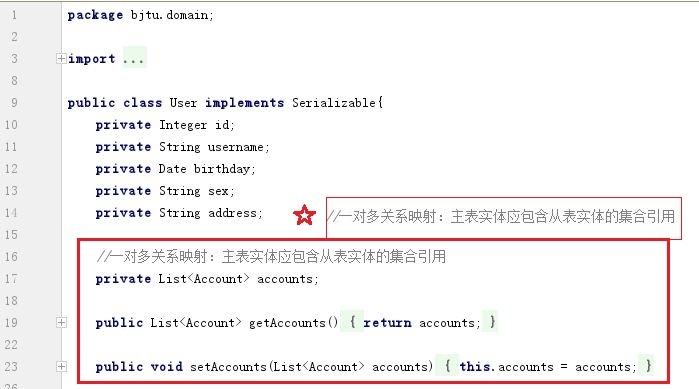
2)其次修改UserDao.xml查询配置文件
3. 多对多查询
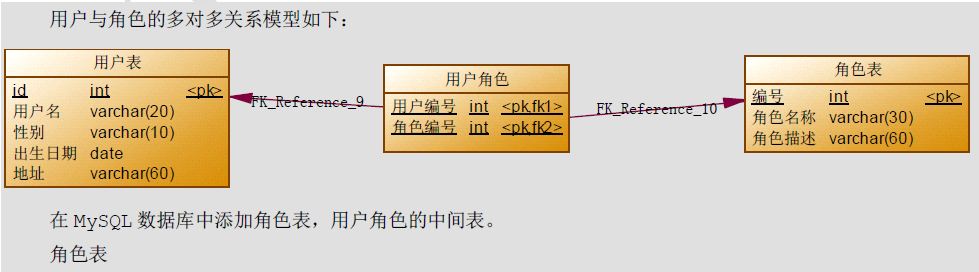
示例描述
示例:用户和角色
一个用户可以有多个角色
一个角色可以赋予多个用户
步骤:
1、建立两张表:用户表,角色表
让用户表和角色表具有多对多的关系。需要使用中间表,中间表中包含各自的主键,在中间表中是外键。
2、建立两个实体类:用户实体类和角色实体类
让用户和角色的实体类能体现出来多对多的关系
各自包含对方一个集合引用
3、建立两个配置文件
用户的配置文件
角色的配置文件
4、实现配置:
当我们查询用户时,可以同时得到用户所包含的角色信息
当我们查询角色时,可以同时得到角色的所赋予的用户信息
这个多对多的搜索主要是修改SQL语句,映射文件.xml的配置和一对多查询操作类似
* UserDao.xml配置文件,RoleDao.xml文件配置类似
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="bjtu.dao.RoleDao">
<!--定义User的resultMap-->
<resultMap id="roleMap" type="bjtu.domain.Role">
<id property="roleId" column="rid"></id>
<result property="roleName" column="role_name"></result>
<result property="roleDesc" column="role_desc"></result>
<collection property="users" ofType="bjtu.domain.User">
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="address" property="address"></result>
<result column="sex" property="sex"></result>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!--配置查询所有-->
<select id="findAll" resultMap="roleMap">
select u.*, r.id as rid, r.role_name, r.role_desc from role r
left outer join user_role ur on r.id = ur.rid
left outer join user u on u.id = ur.uid
</select>
</mapper>
Mybatis的缓存
Mybatis中的延迟加载
问题:在一对多中,当我们有一个用户,它有100个账户。 在查询用户的时候,要不要把关联的账户查出来? 在查询账户的时候,要不要把关联的用户查出来? 在查询用户时,用户下的账户信息应该是,什么时候使用,什么时候查询的。 在查询账户时,账户的所属用户信息应该是随着账户查询时一起查询出来。什么是延迟加载?
在真正使用数据时才发起查询,不用的时候不查询。按需加载(懒加载)
什么是立即加载?
不管用不用,只要一调用方法,马上发起查询。
在对应的四种表关系中:一对多,多对一,一对一,多对多。 一对多,多对多:通常情况下我们都是采用延迟加载; 多对一,一对一:通常情况下我们都是采用立即加载。
Mybatis中的缓存
什么是缓存
存在于内存中的临时数据。
为什么使用缓存
减少和数据库的交互次数,提高执行效率。
什么样的数据能使用缓存,什么样的数据不能使用
适用于缓存: 经常查询并且不经常改变的。 数据的正确与否对最终结果影响不大的。 不适用于缓存: 经常改变的数据 数据的正确与否对最终结果影响很大的。 例如:商品的库存,银行的汇率,股市的牌价。Mybatis中的一级缓存和二级缓存
一级缓存: * 它指的是Mybatis中SqlSession对象的缓存。 * 当我们执行查询之后,查询的结果会同时存入到SqlSession为我们提供一块区域中。该区域的结构是一个Map。当我们再次查询同样的数据,mybatis会先去sqlsession中查询是否有,有的话直接拿出来用。 * 当SqlSession对象消失时,mybatis的一级缓存也就消失了。 * 如果sqlSession去执行commit操作(执行插入、更新、删除),清空SqlSession中的一级缓存,这样做的目的为了让缓存中存储的是最新的信息,避免脏读。 二级缓存: * 它指的是Mybatis中SqlSessionFactory对象的缓存。由同一个SqlSessionFactory对象创建的SqlSession共享其缓存。 * 二级缓存的使用步骤: * 第一步:让Mybatis框架支持二级缓存(在SqlMapConfig.xml中配置) * 第二步:让当前的映射文件支持二级缓存(在IUserDao.xml中配置) * 第三步:让当前的操作支持二级缓存(在select标签中配置)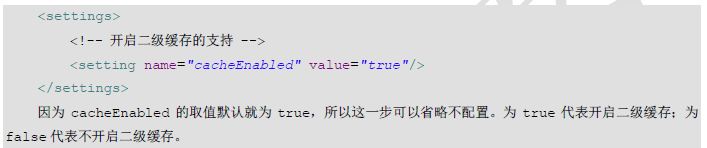
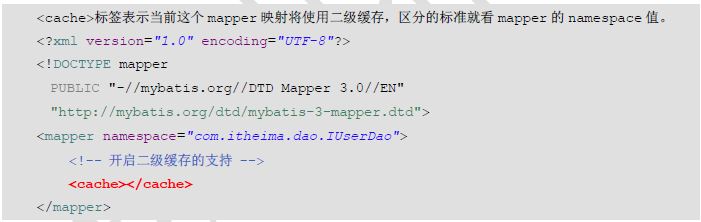

Mybatis中的注解开发
这几年来注解开发越来越流行,Mybatis也可以使用注解开发方式,这样我们就可以减少编写Mapper(即UserDap.xml、AccountDao.xml等配置文件)映射文件了。在Mybatis中只能使用映射配置文件和注解配置一种方式,所以使用注解配置时,应将映射配置文件移除。
1. 单表的CUDA操作
首先针对单表的CUDA操作,只需要在UserDao接口文件的相关方法上添加配置即可。Mybatis中有四种SQL相关的语句配置:
- @Insert: 实现新增
- @Update: 实现更新
- @Delete: 实现删除
- @Select: 实现查询
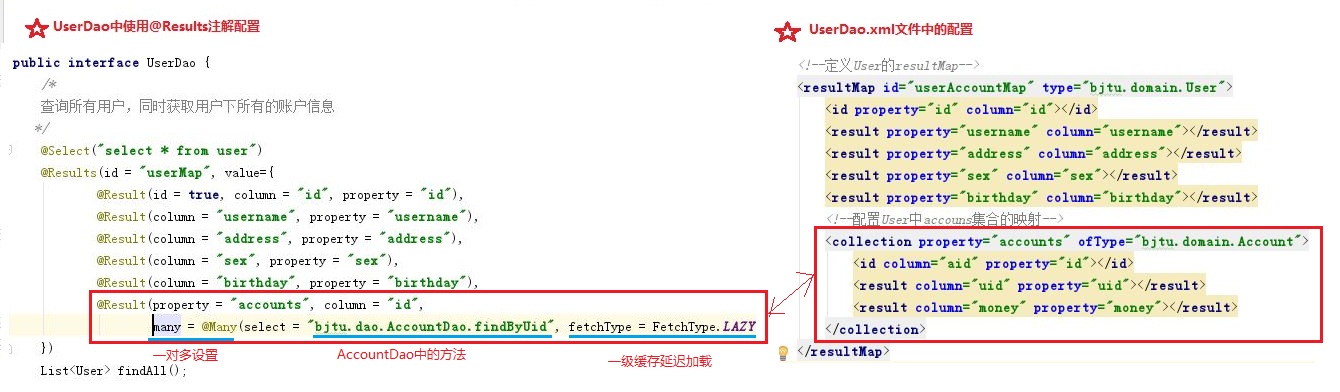
以User类的接口UserDao为例,程序改写如下:
public interface UserDao {
/*
查询所有用户,同时获取用户下所有的账户信息
*/
@Select("select * from user")
@Results(id = "userMap", value={
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "username", property = "username"),
@Result(column = "address", property = "address"),
@Result(column = "sex", property = "sex"),
@Result(column = "birthday", property = "birthday"),
})
List<User> findAll();
/**
* 按ID查询用户信息
* @param userID
*/
@Select("select * from user where id = #{uid}")
@ResultMap(value = {"userMap"})
User findById(Integer userID);
/**
* 插入保存user
* @param u
*/
@Insert("insert into user(username,address,sex,birthday) values(#{username},#{address},#{sex},#{birthday})")
@ResultMap(value = {"userMap"})
void saveUser(User u);
/**
* 更新信息
* @param u
*/
@Update("update user set username=#{username},address=#{address},sex=#{sex},birthday=#{birthday} where id=#{id}")
@ResultMap(value = {"userMap"})
void updateUser(User u);
/**
* 删除用户
* @param userID
*/
@Delete("delete from user where id = #{id}")
@ResultMap(value = {"userMap"})
void deleteUser(Integer userID);
/**
* 按名称模糊查询用户信息
*/
@Select("select * from user where username like #{username}" )
@ResultMap(value = {"userMap"})
//@Select("select * from user where username like '%${value}%'" )
List<User> findByName(String username);
/**
* 聚合函数:查询总记录条数
*/
@Select("select count(id) from user")
@ResultMap(value = {"userMap"})
int findTotal();
}
- 只需要在方法之上添加 @Select(“SQL语句”),@Insert(“SQL语句”),@Update(“SQL语句”),@Delect(“SQL语句”)。
- 另外,若User类中的属性与数据库中user表的列名不一致,需要增加 @Results() 注解配置,类似于UserDao.xml中的
配置。 
2. 多表操作配置
一对一配置

一对多配置