Remove Nth Node From End of List
Description
Given a linked list, remove the n-th node from the end of list and return its head.
Example
Given linked list: 1->2->3->4->5, and n = 2.
After removing the second node from the end, the linked list becomes 1->2->3->5.
Solution
方法一:两次扫描
第一次扫描确定链表的长度,第二遍扫描删除指定的节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
//***********自己实现的方法*****************//
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode t = head;
int len=0;
int point=1;
while(t != null) {
len++;
t = t.next;
}
if(len - n == 0) {
return head.next;
}
t=head;
while(point < len-n){
t = t.next;
point++;
}
t.next=t.next.next;
return head;
}
}
方法优化提升
首先设置一个指向head的“dumpy”结点,设置这个结点是为了简化一些特殊的情况,比如链表只有一个结点点或者要删除的节点是第一个结点。
第一次扫描链表得到链表的长度L
第二次扫描先指向dumpy,从开始移动到第 L-n 个结点,使第 L-n 个结点指向第 L-n+2 个结点。
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
int length = 0;
ListNode first = head;
while (first != null) {
length++;
first = first.next;
}
length -= n;
first = dummy;
while (length > 0) {
length--;
first = first.next;
}
first.next = first.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
算法分析
时间复杂度:O(L) L为链表的长度
空间复杂度:O(1)
方法二:一次扫描法
一次扫描的方法是通过设置两个指针 first 和 second,首先 first 指针从开始移动 n+1 次,second 指针在起始的位置。这样使两个指针始终保持 n 个节点的距离向前移动,当 first 指针指向节点为空的时候,second 指针处在倒数第 n+1 的位置,此时可以删除目标位置的节点。
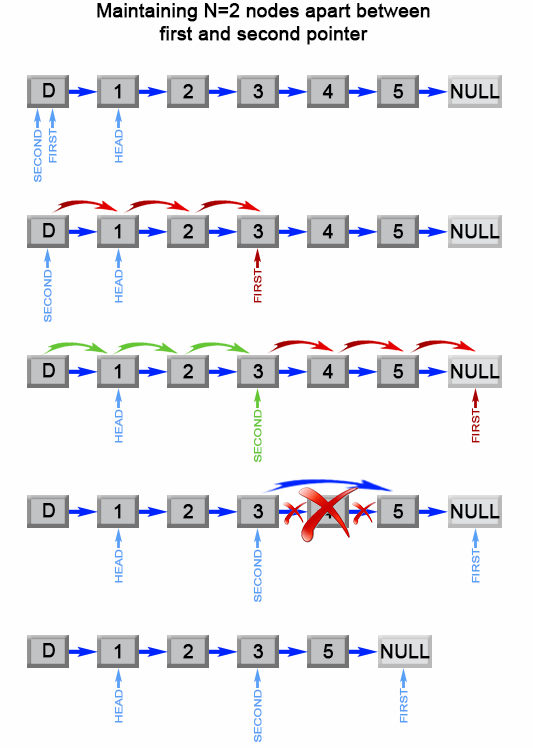
public ListNode removeNthFormEnd(ListNode head,int n) {
ListNode dumpy = new ListNode(0);
dumpy.next = head;
ListNode first = head;
ListNode second = head;
for(int i=1;i<n+1;i++) {
first=first.next;
}
while(first != null) {
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
second.next = second.next.next;
return dumpy.next;
}
算法分析
时间复杂度:O(L) L为链表的长度
空间复杂度:O(1)
Merge Two Sorted Lists
Description
Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new list. The new list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Example
Input: 1->2->4, 1->3->4
Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4
Solution
方法一:迭代法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode cur = new ListNode(0);
ListNode relt = cur;
while(l1!=null && l2!=null) {
if(l1.val < l2.val) {
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else {
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if(l1==null) cur.next=l2;
if(l2==null) cur.next=l1;
return relt.next;
}
}
方法二:递归法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1==null) return l2;
if(l2==null) return l1;
if(l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next=mergeTwoLists(l1.next,l2);
return l1;
}else {
l2.next=mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
Merge k Sorted Lists
Description
Merge k sorted linked lists and return it as one sorted list.
Example
Input:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
Solution
分而治之方法
方法描述:这是一种递归的方法,思想就是将k个链表两两合并,如下图所示。
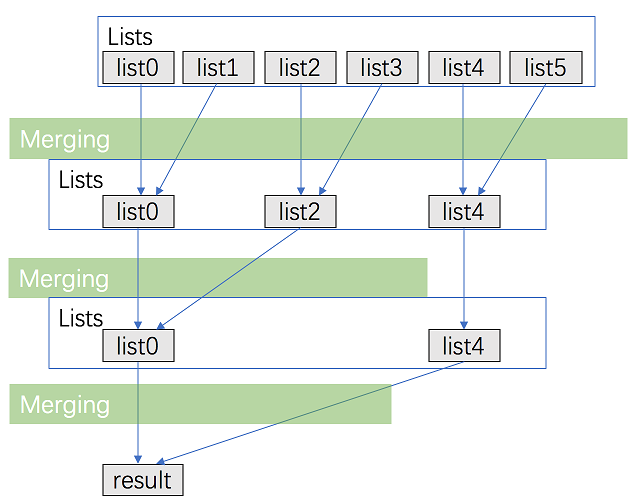
public class MergeKSortedLists {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
return merge(lists,0,lists.length-1);
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode[] lists,int left,int right) {
if(left == right) {
return lists[left];
}
if(left < right) {
int mid = (right + left)/2;
ListNode l1 = merge(lists,left,mid);
ListNode l2 = merge(lists,mid+1,right);
return mergeTwoLists(l1,l2);
}else {
return null;
}
}
private ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1,ListNode l2) {
if(l1 == null) return l2;
if(l2 == null) return l1;
if(l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next,l2);
return l1;
}else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
算法分析
时间复杂度:O(N*lgk),N是两个链表节点总数,lgk是分治算法递归实现的复杂度.
空间复杂度:O(1)
Swap nodes in pairs
Description
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
Example
Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
Soution
迭代法
public class SwapNodesInPairs {
public ListNode swappairs(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null) return head;
ListNode dumpy = head.next;
while(head!=null && head.next!=null) {
ListNode first = head.next;
ListNode second = head.next.next;
first.next = head;
head.next = (second==null || second.next==null) ? second : second.next;
head = second;
}
return dumpy;
}
}
算法分析
时间复杂度:O(n),n为链表的长度
空间复杂度:O(1)
递归法
public class SwapNodesInPairs {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null) return head;
ListNode first = head.next;
ListNode second = head.next.next;
first.next = head;
head.next = swapPairs(second);
return first;
}
}
Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Description
Given a linked list, reverse the nodes of a linked list k at a time and return its modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes in the end should remain as it is.
Example
Given this linked list: 1->2->3->4->5
For k = 2, you should return: 2->1->4->3->5
For k = 3, you should return: 3->2->1->4->5
Soluton
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
/* if(head == null)
return null;
if(k == 1)
return head;*/
ListNode dumpy = new ListNode(-1);
dumpy.next = head;
ListNode temp = head;
int count = 0;
while(temp!=null && count!=k) {
temp = temp.next;
count++;
}
if(count == k) {
temp = reverseKGroup(temp,k);
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while(k > 1) {
pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next = dumpy.next;
dumpy.next = cur;
cur = pre.next;
k--;
}
pre.next = temp;
}
return dumpy.next;
}
}
算法分析
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
Reverse Linked List
实现翻转链表的功能
方法一:原地翻转
public class ReverseLinkedList {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
//原地翻转法
if(head == null)
return head;
ListNode dumpy = head;
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while(cur != null) {
pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next = dumpy.next;
dumpy.next = cur;
cur = pre.next;
}
return dumpy.next;
}
}
方法二:建立新链表,插入式翻转
public class ReverseLinkedList {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
//建立新链表,添加节点翻转法
if(head == null)
return head;
ListNode dumpy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode nex = cur.next;
cur.next = dumpy.next;
dumpy.next = cur;
cur = nex;
}
return dumpy.next;
}
}
有序链表转换二叉搜索树
题目描述:
给定一个单链表,其中的元素按升序排序,将其转换为高度平衡的二叉搜索树。
本题中,一个高度平衡二叉树是指一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1。
解题思路
如何找出这样的一个根节点呢?我们可以找出链表元素的中位数作为根节点的值。
这里对于中位数的定义为:如果链表中的元素个数为奇数,那么唯一的中间值为中位数;如果元素个数为偶数,那么唯二的中间值都可以作为中位数,而不是常规定义中二者的平均值。
根据中位数的性质,链表中小于中位数的元素个数与大于中位数的元素个数要么相等,要么相差 11。此时,小于中位数的元素组成了左子树,大于中位数的元素组成了右子树,它们分别对应着有序链表中连续的一段。在这之后,我们使用分治的思想,继续递归地对左右子树进行构造,找出对应的中位数作为根节点,以此类推。
方法一:分治
1) 有序链表查找中位数-快慢指针法:
找出链表中位数节点的方法多种多样,其中较为简单的一种是「快慢指针法」。初始时,快指针 fast 和慢指针 slow 均指向链表的左端点 left。我们将快指针 fast 向右移动两次的同时,将慢指针 slow 向右移动一次,直到快指针到达边界(即快指针到达右端点或快指针的下一个节点是右端点)。此时,慢指针对应的元素就是中位数。
2) 在找出了中位数节点之后,我们将其作为当前根节点的元素,并递归地构造其左侧部分的链表对应的左子树,以及右侧部分的链表对应的右子树。